 |
Direct Graphical Models
v.1.7.0
|
 |
Direct Graphical Models
v.1.7.0
|
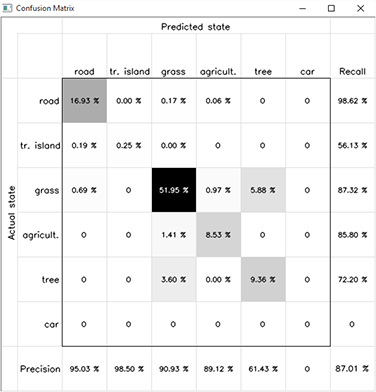
DGM library has a rich set of tools for visualizing the data, intermediate and final results, as well as for interaction with created figures. It also provides tools for analyzing the classification accuracy. In this example we took the Demo Train tutorial, simplified the training sections and expanded the visulaization part. First we estimate the quality of classification with confusion matrix, then we visualize the feature distributions for defined classes in the training dataset as well as the node and edge potentials. For user interaction capacity we define additional functions for handling the mouse clicks over the figures.
| 
| 
| 
|
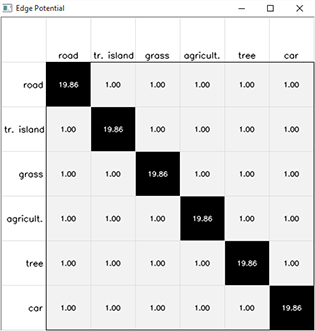
Mouse Handler for drawing the node and edge potentials
This mouse handler provides us with the capacity of user interaction with the Solution window. By clicking on the pixel of the solution image, we can derive the node potential vector from the graph node, associated with the chosen pixel, and visualize it. In this example, each graph node has four edges, which connect the node with its direct four neighbors; we visualize one edge potential matrix, corresponding to one of these four edge potentials. The visualization of the node and edge potentials helps to analyze the local potential patterns.
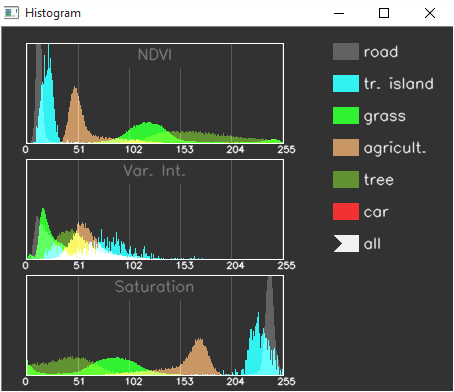
Mouse Handler for drawing the feature distribution histograms
This mouse handler allows for user interaction with Histogram window. Its capable to visualize the feature distributions separately for each class. User can chose the needed class by clicking on the color box near to the class name. These feature distributions allow for analyzing the separability of the classes in the feature sapce.
Starting from the version 1.5.1 this mouse handler is built in the VIS module. Thus, no extra code is needed.